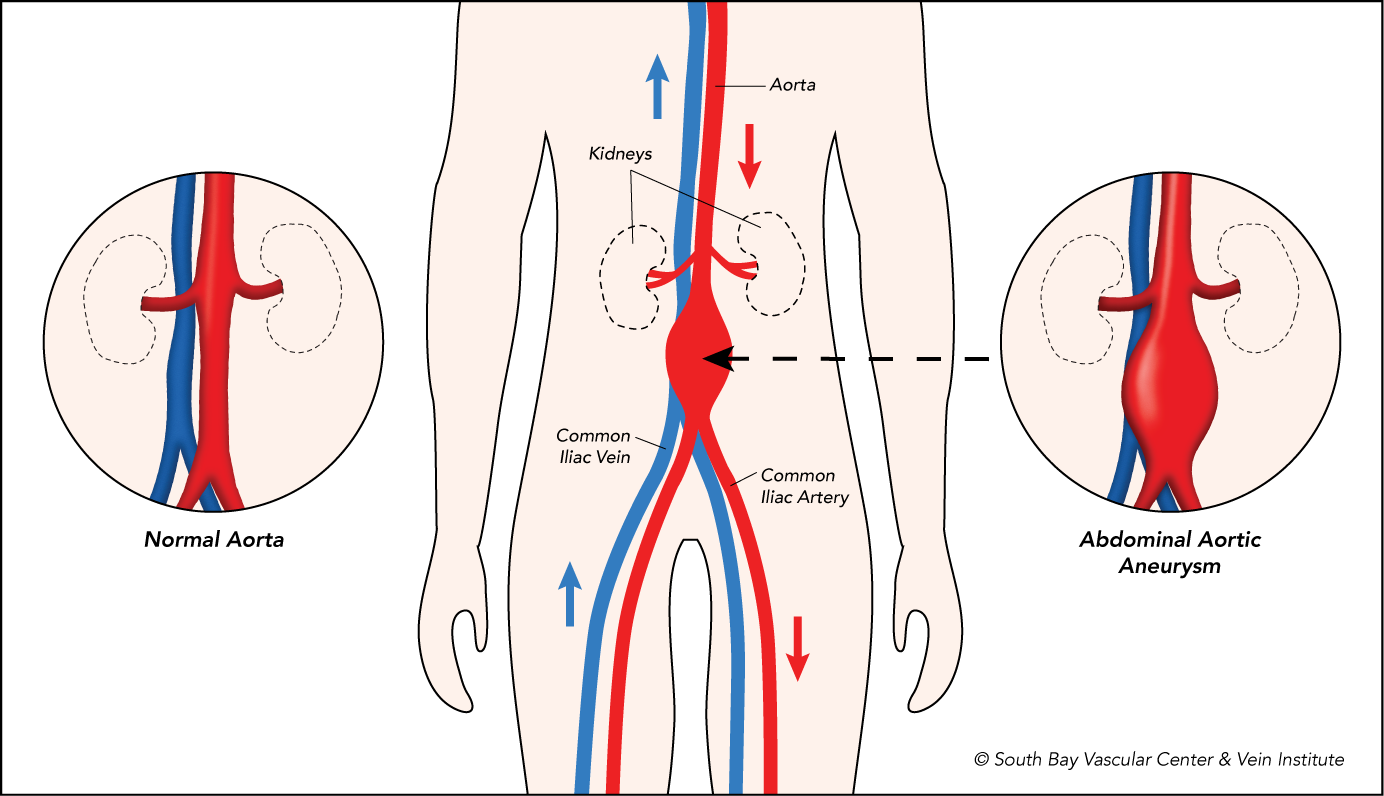
Last week I began a description of the medications that vascular surgeons use with a blog post on drugs used for anticoagulation. This week, I want to describe a group of medications that also thin the blood, albeit through a different mechanism. As discussed last week, the coagulation cascade works to turn the blood from a liquid to a solid. A special group of cells in the blood mixed with red blood cells called platelets works simultaneously with the coagulation cascade to serve as the glue so to speak between clumps of red blood cells. This bond that platelets facilitate with clotted blood helps clot to attach and build upon other collections of clot, thereby facilitating the control of bleeding that the clotting system was designed for.
Obviously, in the case of vascular surgery we often times want to prevent blood clotting from occurring. The main agents we use are aspirin and plavix (clopidogrel). In the early 2000s literature from interventional cardiology for minimally invasive heart procedures found that placing patients on aspirin and plavix together reduced the incidence of recurrent heart attacks as well as death. This literature from cardiology has been extrapolated to the lower extremity circulation and allows the interventions we perform in the lower extremities to fix blood flow to stay open for a long period of time. In addition to the use of aspirin and plavix for lower extremity arterial blockages, we also use it in patients who have had a stroke in order to help prevent them from having another stroke.
Aspirin is a low strength blood thinner that patients can take orally as an 81 mg tablet once a day. In the body aspirin blocks a specific enzyme called cyclooxygenase. When cyclooxygenase is inhibited, the enzyme cannot help to produce chemicals in the blood called prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are normally responsible for creating an environment that stimulates the clotting of blood via complex but mild mechanisms. Studies have shown generally that patients with cardiovascular disease have a lower incidence of death, stroke, and heart attack over time than patients who do not take aspirin. In general, I tend to make sure that all my patients who have peripheral vascular disease take aspirin as a general preventative measure.
Plavix is a much higher strength blood thinner that binds directly to platelets and completely inhibits their function. When used in concert with aspirin, the blood becomes thin enough to prevent the recurrent blockage of vessels that we have opened up.
Overall the large majority of my patients who receive procedures to fix blood flow to the foot are placed on aspirin and plavix. If you think you might benefit from these medications or are in need of a procedure to fix the blood flow to your feet or brain, please do not hesitate to call my office to schedule an appointment!
South Bay Vascular Center and Vein Institute is Silicon Valley’s largest and most trusted Vascular Surgery practice. Serving South Bay communities for over 26 years, Dr Kokinos and her Colleague, Dr Ignatius Lau are the region’s foremost experts in advanced vascular care and provide innovative care for patients suffering from circulation relation problems. At South Bay Vascular Center and Vein Institute our job is to understand the “Why” so that you have real solutions to living a healthy life. Call us today at 408-376-3626 or visit our website at www.southbayvascular.com to learn about what makes us the most referred to vascular surgery clinic in Silicon Valley.
CLICK ON THE LINK BELOW TO READ HOW OUR PATIENTS DESCRIBE THEIR EXPERIENCE AT SOUTH BAY VASCULAR.